Selection of Single Domain Antibodies from Immune Libraries Displayed on the Surface of E. coli Cells with Two β-Domains of Opposite Topologies
PLoS ONE
Volume 8, Issue 9, 23 September 2013, Article number e75126
Salema, V., Marín, E., Martínez-Arteaga, R., Ruano-Gallego, D., Fraile, S., Margolles, Y., Teira, X., Gutierrez, C., Bodelón, G., Fernández, L.Á.
Abstract
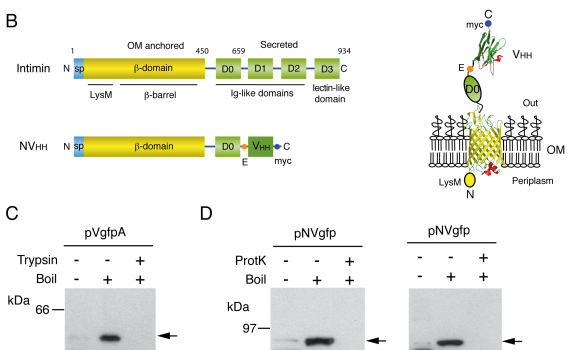
Screening of antibody (Ab) libraries by direct display on the surface of E. coli cells is hampered by the presence of the outer membrane (OM). In this work we demonstrate that the native β-domains of EhaA autotransporter and intimin, two proteins from enterohemorrhagic E. coli O157:H7 (EHEC) with opposite topologies in the OM, are effective systems for the display of immune libraries of single domain Abs (sdAbs) from camelids (nanobodies or VHH) on the surface of E. coli K-12 cells and for the selection of high affinity sdAbs using magnetic cell sorting (MACS). We analyzed the capacity of EhaA and intimin β-domains to display individual sdAbs and sdAb libraries obtained after immunization with the extracellular domain of the translocated intimin receptor from EHEC (TirMEHEC). We demonstrated that both systems displayed functional sdAbs on the surface of E. coli cells with little proteolysis and cellular toxicity, although E. coli cells displaying sdAbs with the β-domain of intimin showed higher antigen-binding capacity. Both E. coli display libraries were screened for TirMEHEC binding clones by MACS. High affinity binders were selected by both display systems, although more efficiently with the intimin β-domain. The specificity of the selected clones against TirMEHEC was demonstrated by flow cytometry of E. coli cells, along with ELISA and surface plasmon resonance with purified sdAbs. Finally, we employed the E. coli cell display systems to provide an estimation of the affinity of the selected sdAb by flow cytometry analysis under equilibrium conditions.