Utility of cardiac biomarkers during adulticide treatment of heartworm disease (Dirofilaria immitis) in dogs
Veterinary Parasitology. Volume 197, Issue 1-2, 18 October 2013, Pages 244-250
Carretón, E. , Morchón, R., González-Miguel, J., Juste, M.C., Simón, F., Montoya-Alonso, J.A.
Abstract
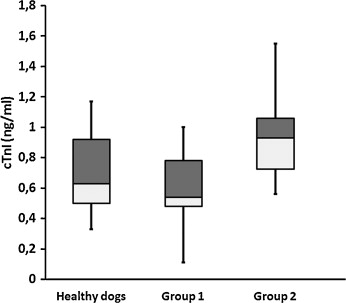
Heartworm disease ( Dirofilaria immitis) is a parasitic disease of dogs and other carnivores, characterized by the presence of adult worms in the pulmonary arteries and right ventricle, leading to pulmonary hypertension which may progress to congestive heart failure. Cardiac biomarkers are biological parameters that can be objectively measured as indicators of pathological processes, or to assess the response to therapeutic interventions. To evaluate the myocardial damage during the adulticide treatment in 15 heartworm-infected dogs with ivermectin, doxycycline and melarsomine, measurements of cardiac troponin I (cTnI), myoglobin, MB isoenzyme of creatine kinase (CK-MB) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST) were carried out on days 0, 60 and afterwards weekly on days 67, 75, 82, 91, 106, 113 and 120. Dogs were divided by low parasite burden (n= 9) and high parasite burden (n= 6). On day 0, dogs with high worm burden showed increased cTnI concentrations (3.62. ±. 4.78. ng/ml) while dogs with low worm burden had concentrations similar to those of healthy dogs (0.78. ±. 0.22. ng/ml), CK-MB concentrations were increased only in dogs with high parasite burden as well (54.4. ±. 54.2. U/l) and 26.6% (4/15) of the dogs showed pathological concentrations of myoglobin. On day 91, most dogs showed pathological concentrations of myoglobin, CK-MB and AST, probably due to the myositis associated to the intramuscular injection of melarsomine. The rest of the measurements made in the study, the biomarkers concentrations were within normal values, except for cTnI in dogs with high parasite burden, which remained above reference concentrations for healthy dogs during all the study. The evaluation of cardiac biomarkers seems to be a helpful test in the assessment of the myocardium in dogs with heartworm disease during the adulticide treatment.