Cross-sectional study on prevalence of Trypanosoma evansi infection in domestic ruminants in an endemic area of the Canary Islands (Spain)
Preventive Veterinary Medicine
Volume 105, Issue 1-2, 1 June 2012, Pages 144-148
Rodríguez, N.F., Tejedor-Junco, M.T. , González-Martín, M., Santana del Pino, A., Gutiérrez, C.
Abstract
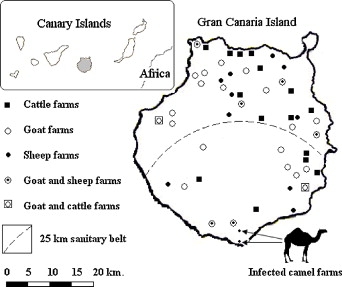
Trypanosoma evansi is the most widely spread of the pathogenic African trypanosomes of animals. The disease (surra) was first diagnosed in the Canary Islands in a dromedary camel in 1997; thus, a control plan was implemented achieving the eventual eradication of T. evansi from most of the infected areas in the Archipelago. However, a little area remains still infected despite the use of the same control measures. To evaluate possible reservoirs in the area a representative sample of domestic ruminants was examined by serological, parasitological and molecular tests. Of a total of 1228 ruminants assessed, 61 (5%) were serologically positive (7 cattle, 21 goats, 33 sheep), but T. evansi could be demonstrated in none of them. According to FreeCalc assessment, cattle and goat populations would be free from disease; however, the results from sheep are not adequate to conclude that the population would be free from disease. As a conclusion, surveillance must be exercised on ruminant farms in the surroundings of the infected area in order to evaluate the possible extension of the disease and their potential role as reservoirs of T. evansi.